Fixed and satellite systems and radars
A fixed system consists of stations with unique locations, which include P-P microwave links, P-MP Microwave links, telemetry, radionavigation, radars, coastal stations and airport stations.
Microwave point-to-point links are directed connections between predetermined fixed locations. Links can be used for the distribution of broadcast stations to transmission points, for connecting base stations of mobile systems, for connecting fixed telephone service exchanges, and for data and voice connections between fixed locations in private systems.
Microwave point-to-multipoint links are directed connections between one and several predetermined fixed locations. Systems are used like infrastructure for the distribution of broadcast stations to transmission points or for the interchange of programmes for connecting mobile base stations and fixed telephone service exchanges.
Telemetry is a system of directed links between predetermined fixed locations, which are used for transferring small amounts of data. Typical use is in water supply and sanitation systems (connections of pumping stations and reservoirs with central management).
Radionavigation is a system for establishing one's own position, composed of receivers and radio stations at fixed locations. For the receivers in the satellite radionavigation there is no need to obtain a decision on awarding radio frequencies. Radars are radio stations intended for establishing the position of objects in space.
Coastal stations are fixed stations for voice and data communication with systems on ships.
Airport stations are fixed stations for voice and data communication with systems on airplanes. Radio frequencies used by individual services on the airport are defined as private networks.
Satellite systems include terrestrial stations in satellite systems and SNG/OB. Terrestrial stations are fixed stations for voice and data communication with satellite systems. SNG/OB are fixed stations for voice and data communication with satellite systems for journalistic purposes.
The applications are available here.
Stations on ships and airplanes
A station on a ship is a radio station for communication between a ship and a radio station on land, while a radio station on an airplane serves for communication between the airplane and a terrestrial radio station. To use radio stations on ships or airplanes it is necessary to receive license or a Decision on awarding radio frequencies (DARF).
Radio stations on ships and airplanes can operate in individual frequency bands, in accordance with international agreements. The license has the data on international identification of an individual station and the installed radio equipment (service, type, serial number).
Ships
Owners of ships specified in the Maritime Code require a license. A condition for issuing a license is the data on ship registration – registration number and ship name. The Agency issues a decision after receiving the application and assigning the call sign and the MMSI number, and after the data are then submitted to the International Telecommunications Union (ITU). The Agency does not assign the EPIRB number, but merely enters it on the license.
The call sign and the MMSI number set by the Agency are issued based on an application that the ship's owner and/or user submits to the Agency. The holder of an issued radio license with a set call sign and an MMSI number for a ship radio station is also obligated to pay for using the radio frequencies in the maritime mobile service.
Airplanes
All airplane owners require a license, and the condition for issuing a license is the data on the airplane's registration. The Agency assigns the call sign and issues a license based on an application.
The call sign is issued by the Agency are issued based on an application that the airplane's owner and/or user submits to the Agency. The holder of an issued radio license with a set call sign for an airplane radio station is also obligated to pay for using the radio frequencies in the aeronautical mobile service.
Radio amateur call signs
A radio amateur is a person who uses radio frequencies for self-education, communication and technical research. Anybody who wants to become a radio amateur must first pass the radio amateur examination at the Association of Radio Amateurs of Slovenia. Then they must obtain a license, which is issued by the Agency based on an application. With the license every radio amateur receives their own call sign.
It is allowed to use the frequencies specified in the General Act on radio frequency utilisation plan, which are reserved for radio amateur or radio amateur satellite applications. A radio amateur always identifies themselves in the system using their call sign.
The applications are available here.
Radio equipment
CE logo on equipment:
The "CE" logo means that the equipment is compliant and can be used in the Republic of Slovenia.
Radio terminals and short-range devices (SRD) are used without a Decision on awarding radio frequencies in the scope of class 1 radio equipment and in accordance with the Radio frequency utilization plan (additional table A.2) – RFUP.
If there are any limitations of use or requirements for a license for use for radio equipment, as defined in Article 10(10) of the Directive 2014/53/EU, the radio equipment packaging must clearly and visibly display the following sign:

and the word "Omejitve" (Limitations) or "Zahteve"(Requirements) in Slovenian. It is also obligatory to list the abbreviations of the member states (as in the examples below) where such limitations or requirements are in effect:
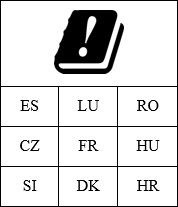

If there are any limitations of use or requirements for a license for use for radio equipment, as defined in Article 10(10) of the Directive 2014/53/EU, the user manual accompanying the radio equipment must list in the language that end users can understand easily and which is set by the relevant member state the member states and geographical areas of these member states where such limitations or requirements are in effect, and types of limitations or requirements used in each member state, and in each geographic area of a member state (Implementing regulation of the Commission (EU) 2017/1354).
Limitations and requirements for using radio equipment in the territory of the Republic of Slovenia are defined in detail by the Rules on radio equipment (issued on the basis of the Technical Requirements for Products and Conformity Assessment Act (ZTZPUS-1)) and the Radio frequency utilization plan – RFUP (issued based on the Electronic Communications Act (ZEKom-1)).